Justice



This President’s Day, about 20 church leaders, sympathizers, and undocumented immigrants were arrested in front of the White House as part of an act of civil disobedience to protest the nearly 2 million people who have been deported under President Obama.
The core group and about 40 supporters gathered around 1 p.m. on Monday afternoon in Lafayette Park in front of the White House. They held signs that said, “Praying for Relief” and “#Not1moredeportation,” and sang hymns in between short megaphoned speeches that told personal stories. They called for immigration reform. “Not one more, not one more,” they chanted together in both English and Spanish.
The event was organized by Bishop Minerva G. Carcaño of the United Methodist Church, who was the first Hispanic woman to be elected to her position.

There are so many people that have gone before me, people that have sacrificed their lives in pursuit of justice and equality. Because of this, I feel a deep sense of commitment to honor them by standing for some of the same things that they did. I am in complete awe of two things that connect deeply for me. The first is the cross and how Jesus gave his life for us all. The second is my ancestors who somehow understood Jesus’ sacrifice and passed it onto me through intense persecution.
I can’t say that I know persecution like my parents, grandparents, and great-grandparents knew. I have been back to southern Alabama many times for family reunions and visited slave graveyards where relatives are buried. This compels me to be and do more with my life. I can’t say I understand why Jesus would choose to become human, walk this earth as a human being, and then die at the hands of his own creations to save those who were crucifying him. However, I do know it pushes me to be and do more with my life. I feel like I would let them down somehow if I didn’t take responsibility for addressing injustice with my life.
My life is not my own. I am the product of sacrifice. I am here because of those who saw beyond themselves and thought personal sacrifice was worth giving up to allow justice to take hold. I am here because Jesus modeled something completely illogical on the cross and then some of my ancestors took that example seriously and repeated it. I have no real right to the life I live. My only recourse is to continue the tradition handed to me in the same way.


America’s justice system is broken.
Our jails are overflowing, people are receiving life sentences for minor crimes under three strikes laws, racial disparities leave minority populations disproportionately represented in the incarcerated population, and we’re so obsessed with killing that we’re now using untested concoctions of drugs that recently took a condemned inmate more than 20 minutes to finally die.
Our system isn’t working.
It might surprise you however, to understand how we arrived at such a broken justice system.
We got here because of poor theology.
WHEN I FOUND out years ago that most early Pentecostal denominations had been committed to nonviolence—including the Assemblies of God, the denomination of my heritage—I thought it was about the dumbest thing I’d ever heard. Not kill for the United States of America (or any country)?
Then I stumbled upon the Pentecostal Evangel, a weekly magazine of the Assemblies of God (USA), which published these revealing words during World War I:
From the very beginning the [Pentecostal] movement has been characterized by Quaker principles. The laws of the Kingdom, laid down by our elder brother, Jesus Christ, in the Sermon on the Mount, have been unqualifiedly adopted, consequently the movement has found itself opposed to the spilling of the blood of any man.
This was new to me. I was reared in a U.S. Pentecostalism that taught intense loyalty to the United States and deep pride in combatant military service. Where did this hidden history of Pentecostal nonviolence come from?
Reading other early accounts of Pentecostal peacemaking prompted me to further examine where it had gone and whether it could re-emerge. It would also challenge and deconstruct my understanding of Christianity.
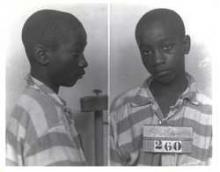
The difficulty of restorative justice, is that some things simply can’t be restored.
Certainly, not 14-year-old George Stinney. He’s been dead almost 70 years.
We can however, restore his name — and sometimes, that’s all restorative justice can do. Restorative justice works to make whole what has been unjustly lost and reassemble that which has been unjustly broken, to the greatest degree humanly possible. While we can’t restore 14-year-old George to life, we can both restore his name and work to restore the community responsible for his death.
Often we forget that restorative justice isn’t just about restoring the one who was wronged; the one who committed the wrong is also need of restoration. In this case, the latter is the state of South Carolina.

“GOD CREATED the world and we created borders.”
That obvious recognition was shared at a recent consultation in Quito, Ecuador, between North American and Latin American churches on “Faith, Economy, and Migration.” Felipe Adolf, president of the Latin American Council of Churches, shared that conclusion on how issues of migration and reform are global and not just local.
It’s very easy to see the problems confronting our nation and feel as though the challenges facing the rest of the world are simply too much to bear. Continuing poverty and unemployment, discrimination of all kinds, and wars and rumors of wars fill our newsfeeds, papers, and TV screens. But it’s naïve and narrow to think this way. Many of the threats we face are global in nature and don’t know any boundaries. Through our economies and consumption habits, media, travels and migrations, and for Christians in particular our faith, we are inextricably connected with men and women around the world. It’s always been important, but now especially so, to think globally when it comes to faith and justice.
Sojourners has a long history of doing this very thing. We started as a little group of two kinds of people—those who had grown up conservative evangelicals and were deeply frustrated with the lack of attention to issues of justice and peace, and those who had just come to faith from the student movements and counterculture of the 1960s and ’70s. We met at Trinity Evangelical Divinity School and began to study and pray through the scriptures about injustice, war, and poverty. The Vietnam War was raging, and we were looking for a biblical understanding of the events of our time.

Overheard on a Facebook conversation last week: “There is really not much difference between compassion and pity when it comes to being on the receiving end of it.” This thought gave me pause as I consider compassion to be a central tenet of biblical justice, and yet, I experience this to be true. We use the fancy spiritual term of “compassion” when the gist of the sentiment is, indeed, pity.
The above conversation rose out of a discussion on the viral story of Pope Francis kissing the disfigured man. The media reporting the story highlights the compassion of the Pope, how his actions are pushing outside the box of the papacy, and how revolutionary his love was. Other than a brief medical description of the disfigured man’s disease, there is no additional information on who he is, where he lives, or whether he has a family. We are not even given his name. The buzz generated by this story arises out of an awed respect for someone who could even consider touching such a pitiful, nameless person. I can’t help but wonder how this man feels to have the world captivated by somebody showing love to himself. It seems to me his deformity has been made into a public spectacle.

It’s a new year, and Congress is back in session.
One of the top issues expected to be debated in 2014 is a hike to the federal minimum wage. 13 states have instituted wage increases. President Obama has supported raising the minimum wage throughout his presidency. Most recently, he shared his approval of new legislation proposed by Sen. Tom Harkin and George Miller (D-Calif.) that would raise the minimum wage to $10.10, up from it’s current $7.25.
Critics of the Harkin/Miller bill are quick to decry any wage increase. The usual arguments are trotted out to combat progressive pay for low-wage earners. Here are five commonly perpetuated myths about minimum wage. Hopefully, their exploration will shed a more accurate light on this contested issue.

EXECUTE: TO ENACT OR DO. Having grown up in inner-city Chicago, I have fond memories of red fire hydrants, swinging jump ropes, and church robes. During summer, the fire department would open the hydrants. Parents granted the petitions of children to run through the streams of water, soaking our clothes and cooling our backs. And while I never achieved the rhythmic agility to jump Double Dutch, I loved to recite the rhymes, which eventually helped me gain a verbal dexterity like that of my pastor. I wanted one day to have a robe like hers—one that signaled that the words I spoke revealed the reign of God.
Turn the clock back. Some children would hold very different memories of fire hydrants, ropes, and robes. In Birmingham, Ala., in1963, the force of the water injured petitioners for freedom. During the American Revolution, a Virginia justice of the peace named Charles Lynch ordered extralegal punishment for Loyalists to the Crown. The swinging rope became the tool of mob violence. And the “hooded ones” continue to use the label of “Christian” to make a mockery of the vestments of clergy.
Fire hydrants. Ropes. Robes. Execute: to eliminate or kill. Meaning conveyed to the hearer may not at all resemble the intention of the speaker. Often communication requires suspension of what we think in order to listen to the context from which the speaker shares. Reading is no easier a task. Sometimes the same letters forming the same word present entirely different meanings. Justice executed. What does it mean?
The context for the next four weeks exposes what the Lord’s justice requires.
Cynthia Bourgeault explains how we can both seek social justice and do justice to our souls.


We used to sing this song in Sunday School, as far back as I can remember, way back when I was learning to use a big-boy potty and tie my shoes. The little light was our faith in Jesus, and letting it shine was sharing it with others, who didn't know him. Jesus loved the little children, all the children of the world, red and yellow, black and white, they were precious in his sight, Jesus loved the little children of the world. He would make us FISHERS! of men, FISHERS! of men, FISHERS! of men, if we followed him, if we followed him, if we FAW! LOWED! HIM! I should dare to be a Daniel, dare to stand alone, dare to have a purpose firm, dare to make it known. Even if they fed me to the lions.
It took almost 30 years for me to really see "This Little Light" in action. Before that, it was mostly an ideal standard that made me feel guilty for not living up to it, a measuring stick that set me in competition with all the other little lights around me; if I shined a little brighter, you'd try too. But two years before Occupy Wall Street demanded economic reform at the national level, the candles lit in Charlotte, N.C., as hundreds of protestors marched on Bank of America and Wachovia in the fall of 2009. In the midst of the subprime mortgage crisis, with people facing ballooning interest rates and foreclosures on their homes, organizers delivered a theological statement against what they called "usury" — the Old Testament sin of collecting interest from the poor.

Bio: Sister Jean Lait, CSF, is an Anglican Franciscan sister based in San Francisco who protests drones and their effects on children. communitystfrancis.org
1. Why did you decide to stand up against drones?
During WWII, I experienced the bombing of Coventry in England. As a child of 9 years, I slept under the stairs, anxiously waiting for the bombs to drop. Toward the end of the war, flying bombs known as “doodlebugs” were used. These were very similar to drones and were sent from Germany. They were aimed anywhere. These were bombs where you heard a whistle and then it was silent before the bang.
Thinking back on the fear and anxiety I experienced, the whole idea of drone warfare is just immoral to me. No child should ever be that frightened. No child should have to live in a war zone. That kind of trauma affects you, one way or another. You either use that experience for good or otherwise.

Online resources

Laying out a blueprint for the issues that are likely to define his papacy, Pope Francis on Tuesday issued a biting critique of capitalism, calling on world leaders to fight against poverty and for the rich to share their wealth, and urging the media to adjust its priorities.
“How can it be that it is not a news item when an elderly homeless person dies of exposure, but it is news when the stock market loses two points?” Francis asked in an 84-page “apostolic exhortation” that is widely seen as a road map for his papacy akin to a presidential State of the Union address.
“How can we continue to stand by when food is thrown away while people are starving?” he asked. “Today, everything comes under the laws of competition and the survival of the fittest, where the powerful feed upon the powerless. As a consequence, masses of people find themselves excluded and marginalized: without possibilities, without any means of escape.”
If you were on Facebook or Twitter last week, you probably saw the CBS interview with Mandy Patinkin. He’s probably best known for this line from the classic movie The Princess Bride:
“Hello. My name is Inigo Montoya. You killed my father. Prepare to die.”
The Princess Bride was released when I was 16. My friends and I would throw that line back and forth whenever we competed against one another. Monopoly. Basketball. Chess. Nintendo. Rock, paper, scissors. It didn’t matter. Like anyone with a pulse during the late 1980s, we repeated that phrase endlessly. It was our favorite line in the movie.
That and “Mawwiage …”
But that’s not Mandy’s favorite line.