infant mortality
After I blogged about expensive American childcare earlier this week, my daughter Molly directed me to a March of Dimes web page showing the extremely high rate of preterm births in the United States. "Born Too Soon," a 124-page report issued in 2012, "ranks the U.S. 131st in the world in terms of its preterm birth rate of 12.0 per 100 live births, almost tied with Somalia, Thailand, and Turkey. Nearly half a million babies are born too soon in the U.S. each year."
According to a 2009 report from the Centers for Disease Control, "the main cause of the United States’ high infant mortality rate when compared with Europe is the very high percentage of preterm births in the United States" — in spite of the fact that "infant mortality rates for preterm (less than 37 weeks of gestation) infants are lower in the United States than in most European countries." In addition, "infant mortality rates for infants born at 37 weeks of gestation or more are higher in the United States than in most European countries."
"American Way of Birth, Costliest in the World"
That's the headline of an article by Elisabeth Rosenthal in yesterday's New York Times. The article includes a chart comparing childbirth costs in seven countries. In the United States, the average amount paid for a conventional delivery in 2012 was $9,775; for a Caesarean section, it was $15,041. Those are the highest prices for childbirth anywhere in the world.
To get an idea of just how high, I made a chart using the figures in the NYT chart. Childbirth costs in the other six countries range from 21 percent to 43 percent of U.S. costs even though American women typically spend far less time in hospital.
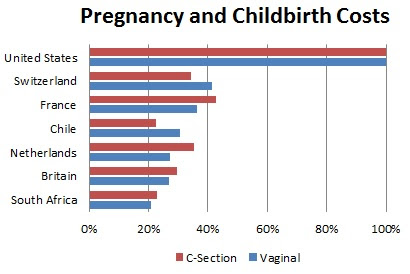
South Africa is so dangerous for childbirth that its graph line would not fit on this blog page. For every 1,000 births, there are 56 infant deaths. For every 100,000 births, there are 400 maternal deaths. [Chart by L. Neff; data from WHO]

LALIBELA, Ethiopia -- You know the images you have in your mind of Ethiopia from 27 years ago? The ones from the nightly news reports on TV about the famine in the Horn of Africa as the death toll mounted and horror stories grew more unfathomable by the day.
Scorched, cracked earth. The carcasses of ematiated, dead cattle lying in the baking sun. Hundreds of thousands of stick-thin refugees wandering in the dust, hoping to have enogh strength to make it to a camp that might have water and food. The babies and children with orange hair and distended stomachs -- indications that they were in the advanced stages of malnutrition and starvation.
I am happy to report that the Ethiopia of 2012 is not the Ethiopia of 1985.
Thanks to global efforts (Live Aid, etc., back in the day), foreign aid, and the very real efforts of the Ethiopian government and people themselves, the land I saw earlier this month looks nothing like those old images in my mind. In fact, parts of the country that we traveled through were so verdent and lush -- farmlands rolling out in various shades of green like a St. Patrick's Day quilt -- that if you'd blindfolded me when I got on the plane and taken the blind of when I stepped of the bus in the rural area outside Bahir Dar near the Sudanese border, I might have thought I was in Ireland's County Kerry rather than Ethiopia's Amhara Region.
Ethiopia is beautiful. In every way. It's people. It's resilience. It's ingenuity and entrepreneurial spirit. In the way it cares for its land and its people, and the way they care for each other and their visitors. There is a spirit in Ethiopia I've experienced only rarely elsewhere. In a word I'd call it HOPE. But it's a hope not based on daydreams and fairytales. It's a hope based in hard work, smart planning, and forward thinking.

I find myself thinking a lot about maternal mortality (and the issues that surround it, like access to contraception) lately, partly because I’ll soon be moving to a country with one of the world’s most dismal maternal mortality rates, and partly because my husband and I aren’t planning to have more biological children, which means that we’re contracepting for the duration.
Also, Nicholas Kristof and Sheryl WuDunn’s Half the Sky movement is gaining even more visibility — PBS’s Independent Lens is creating a series of short films and some longer features on issues raised in their bestselling, well-worth-reading book even as birth control reemerges again and again as a point of contention between Catholic bishops and nuns, between government policy and religious conviction, and even, as Amy Frykholm as suggested, among evangelicals.
Recently I’ve become aware that unwanted pregnancies are nothing new — certainly not the product of a culture that’s “anti-life” or anti-children, as the new-ish evangelical suspicion of birth control has it. In the 1850s, Mathilde Shillock, a German immigrant settled on the Minnesota frontier wrote,
“God has entrusted us with a son...it seems that his father is happy over it, I myself do not wish for any more children, as I look upon life as a heavy burden. [...] pity is all I can offer [this child]. Pity and a feeling of duty towards him to lighten his blameless fate.”