In a perfect world, women can choose to be whomever they want. But there is not yet a country on earth in which that is actually true. That is why we need feminism.
That there’s disagreement over how we talk about women’s empowerment in the U.S. isn’t surprising — feminism is a collection of unique people with unique visions of a good life, trying to figure out how to preserve past and present good, correct past and present wrongs, and forge a new way ahead together.
But it is tragically, perennially clear why speaking up against male-controlled narratives in church or school or novels or movies or business or government, against generations of excused behavior for men and oppression for women, against ongoing systemic injustice is still so crucially necessary.
From reading what these “anti-modern-feminists” have written, I don’t believe any of them would take umbrage with that. It’s a pity, then, they are rejecting the term feminism — their challenges would be great additions to the dialogue. More education and conversation about what feminism is, and how we do it, and where it can go, is clearly needed. Without it, I’m not at all sure how much farther forward we’ll be able to go.
Last week, here in Kabul, the Afghan Peace Volunteers welcomed activist Carmen Trotta, from New York, who has lived in close community with impoverished people in his city for the past 25 years, serving meals, sharing housing, and offering hospitality to the best of his ability. Put simply and in its own words, his community, founded by Dorothy Day, exists to practice “the works of mercy” and to “end the works of war.” We wanted to hear Carmen’s first impressions of traveling the streets of Kabul on his way from the airport to the working class neighborhood where he’ll be staying as the APVs’ welcome guest.
He said it was the first time he’d seen the streets of any city so crowded with people who have no work.
Carmen had noticed men sitting in wheelbarrows, on curb sides, and along sidewalks, unemployed, some of them waiting for a day labor opportunity that might or might not come. Dr. Hakim, the APV’s mentor, quoted Carmen the relevant statistics: the CIA World Fact Book uses research from 2008 to put Afghanistan’s unemployment rate at 35 percent — just under the figure of 36 percent of Afghans living beneath the poverty level. That’s the CIA’s unemployment figure. Catherine James, writing in The Asian Review this past March, noted that “the Afghan Chamber of Commerce puts it at 40%, the World Bank measures it at 56% and Afghanistan’s labor leaders put it at a shocking 86%.”
An independent religious freedom watchdog panel has welcomed the State Department’s annual religious freedom report and its list of the world’s worst offenders, which had laid dormant for three years.
The list of “countries of particular concern” had remained unchanged since 2006 — and hasn’t been formally issued by the State Department since 2011 — when Burma, China, Eritrea, Iran, North Korea, Saudi Arabia, Sudan and Uzbekistan were cited.
In April, the U.S. Commission on International Religious Freedom recommended that the list be doubled to include Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Vietnam, Pakistan, Syria, Iraq, Nigeria, and Egypt. Turkmenistan was the only new addition to this year’s CPC list, bringing the total to nine countries.
The State Department and the independent USCIRF have often been at odds on who makes the list of worst offenders, and in a statement, USCIRF noted the “disappointing omission” of Pakistan in particular.
“Pakistan represents the worst situation in the world for religious freedom for countries not currently designated by the U.S. government as CPCs,” said USCIRF Chair Katrina Lantos Swett.
Paul said, "the foolishness of the cross" not "the stable middle-class lifestyle," if you want my opinion on seminary education, the changing economy, and baptismal identity in general. We bear a responsibility to care for one another as Christians (and beyond) that we have abdicated to the persnickety "marketplace." It's time to talk about holy poverty again, I think.
I can hear my free church friends and colleagues now, "But we don't take a vow of poverty!" It's true. We don't. We remember this historical movement away from the monasteries and the cathedrals, the parish system and the state church. This is an issue of ecclesiology, no question. What I wonder, however, is if in our attempts to not fall into the traps of the past, we simply have settled on the marketplace as our model for ecclesiology. I assume we have.
My degree is a "professional degree," yet within its conceptual framework the notion that I am "professed" is easily lost. I am not called to earn, but to labor, to serve. My work is "worth" nothing. Instead, it is a response to a vocation that in many ways we all share. The wealth of the community affords me the opportunity to respond to that shared call in a particular way. I am not your employee. I am your pastor. I am poor. Any wealth I may posses comes directly from the pockets of others.
A federal appeals court panel in Virginia became the second one this summer to strike down a state ban against same-sex marriage Monday, making it more likely that the Supreme Court will settle the issue as early as next year.
“We recognize that same-sex marriage makes some people deeply uncomfortable,” said Judge Henry Floyd, originally appointed a district judge by George W. Bush and elevated to the circuit court by President Obama. “However, inertia and apprehension are not legitimate bases for denying same-sex couples due process and equal protection of the laws.”
The circuit court has jurisdiction over Virginia, Maryland, West Virginia, North Carolina and South Carolina. The panel’s decision will not take effect until at least Aug. 18 while circuit clerks defending the state’s ban decide whether to appeal to the full appellate court or the Supreme Court.
Like the first appeals court panel to rule on the issue this year in Utah and Oklahoma, the three-judge panel was deeply divided.
When I was a child, I lived in a black-and-white world of all-this or all-that.
Humankind meant my family. The world meant my neighborhood. Religion meant my church. Politics meant my father’s beliefs.
Oh, I was aware that more was out there, but it had little claim on my imagination or loyalties. My world was complete. There were no gray areas, no compromises, no maybes.
That was a child’s view, reality writ small. In time, I advanced beyond it, until the world became large, complicated, and gray, with places beyond imagining, people totally unlike anyone I knew, ideas beyond anything I heard at my parents’ table.
It’s called growing up. Discovering through knowledge and experience that the little I grew up knowing wasn’t enough to know.
We are witnessing today a headlong retreat into the not-knowing and simplistic partisanship of childhood. Ideas that make people uncomfortable are banished. Science that calls faith into question is shouted down. Politics isn’t just hardball, it’s dumb-ball: I must win, at any cost, and you must lose. I am right, and you are wrong. My tribe is the only tribe that has value and rights.
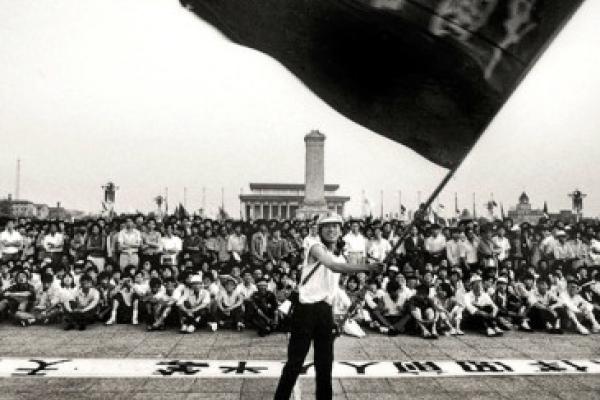
While last month marked the 25th anniversary of China’s silencing freedom in Tiananmen Square, this month China has been cementing this grim legacy — particularly regarding religious freedom.
During the just-concluded month of Ramadan, China denied Uighur Muslim students, teachers, professors, and government employees the freedom to fast and fulfill related duties. With Ramadan coinciding this year with the commemoration of the Communist Party’s founding, Chinese authorities used the occasion to identify fasting Muslims, particularly in Xinjiang province. Those defying the ban have been subject to threats, detention, and arrests.
In recent years, officials have shut down religious sites; conducted raids on independent schools, leading to multiple injuries and even deaths; confiscated religious literature; restricted private study of the Quran; monitored the sermons of imams and forced them to undergo political training; restricted Muslim dress and religious expression; banned children from being brought to mosques; and arbitrarily deemed religious gatherings and activities “illegal.”
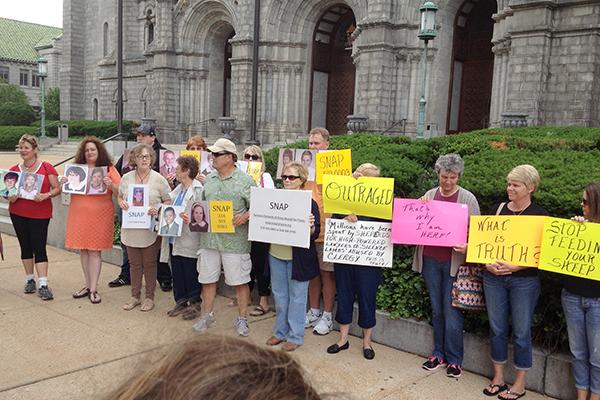
When victims of sexual abuse by Catholic priests first organized into a small band of volunteer activists in the late 1980s, reports of clergy molesting children were still new and relatively few. Most were minimized as anomalies or dismissed altogether — much the way the victims were.
But today, as the Survivors Network of those Abused by Priests, or SNAP, marks its 25th anniversary at a conference in Chicago, its members can take satisfaction in seeing that its claims have been validated, and a few (though hardly all) of its recommendations have been implemented by the church hierarchy.
And instead of facing constant verbal attacks and the occasional angry parishioner spitting on them at a protest, SNAP’s members today are far more likely to receive a handshake and a word of thanks, and maybe even a donation.
SNAP’s advocacy on the Catholic scandal also helped push the reality of sexual abuse into the public consciousness to the point that victims can regularly win in courts and get a hearing in the media, and they are much more likely to come forward to tell their stories, whether they were abused by clergy or by athletic coaches or Boy Scout leaders.
Yet that success is also presenting SNAP with a daunting new challenge as it looks to the future: how to respond to a flood of new inquiries from victims from other faiths and institutions, and how to push for changes beyond the familiar precincts of the Catholic Church.
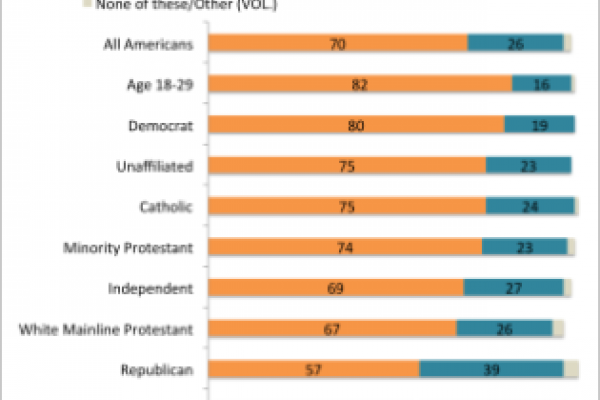
Most Americans say the waves of children crossing into the United States from Central America are refugees fleeing danger at home. And they say the United States should support these children while reviewing their cases, not deport them immediately.
Democrats (80 percent), independents (69 percent), and Republicans (57 percent) favor offering support to unaccompanied children while a process to review their cases gets underway.
Most major religious groups say the same, including white evangelical Protestants (56 percent), white mainline Protestants (67 percent), minority Protestants (74 percent), Catholics (75 percent), and the religiously unaffiliated (75 percent).
(The survey sample of 1,026 adults was not large enough to capture the views of smaller religious groups, such as Jews, Muslims, or Mormons).
“It makes a difference that we are talking about children facing violence and harm,” said Robert P. Jones, CEO of PRRI. “The value of keeping families together cuts across all party lines.”
The first thing that visitors and volunteers see at the Tent of Nations just outside of Bethlehem is a large stone on which are written the words, “We refuse to be enemies.” As Israeli settlements draw ever closer to their land and the Israeli Defense Forces destroy their orchards, the Nassar family continues to pay a heavy price in their practice of Jesus’ teaching, “Love your enemies, do good to those who hate you, bless those who curse you, pray for those who abuse you (Luke 6:27-28).”
The Nassars refuse to divide the world into friends and enemies, challenging the rest of us to do the same.
As a Christian, I was raised to be pro-Israel. Since going to the region many times, I’ve become pro-Palestinian and pro-peace, too, which has led me to explore the narratives of Palestinians as well as Israelis. I grieve the deaths in both Israel and Palestine. Every human life has extraordinary value. The loss of even one life is a loss to all of us.