PORTLAND, Ore. – Future generations could be stripped of mutations such as hereditary blindness or maternal diabetes, after a breakthrough study at Oregon Health & Science University.
But the new technique is also one short step from genetic design of future generations, said Marcy Darnovksy of the California-based Center for Genetics and Society. "These powerful new technologies have a whole bunch of wonderful and appropriate uses – and a number of ways they can be misused.
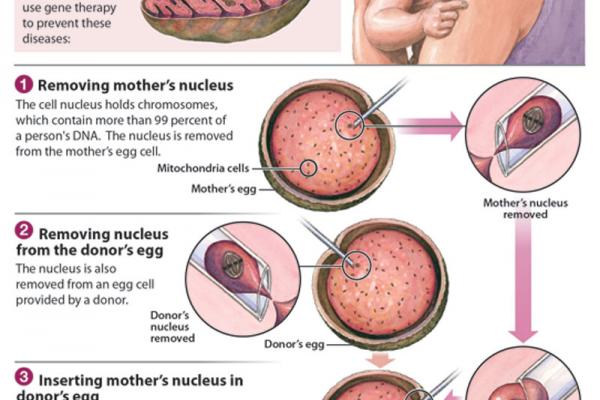
The researchers, led by OHSU biologist Shoukhrat Mitalipov, modified unfertilized eggs for the first time, a technique that offers great promise as well as ethical pitfalls. Such research is banned in many countries.
Three years ago, the Russian-born Mitalipov made headlines with experiments that created monkeys with genetic material from three parents. Now, his team has done it with human cells, setting the stage for possible experiments with humans.
The procedure dealt with what's called mitochondrial DNA, the small part of the cell that turns food into energy. Mitochondrial disorders can lead to neuropathy (a type of dementia) and nervous system disorders such as Leigh disease.
In a study published Wednesday in the journal Nature, the OHSU team described successfully transferring DNA from donor cells into other donor cells, fertilizing the eggs to create 13 tiny early embryos of roughly 100 cells each. These pre-embryos, called blastocysts, were converted to embryonic stem cells for future research.
Key to the technique: replacing the defective mitochondrial DNA with healthy genetic material from the egg of a second woman.
Read the Full Article